ARP Address Resolution Protocol) and Types of ARP
What is ARP?
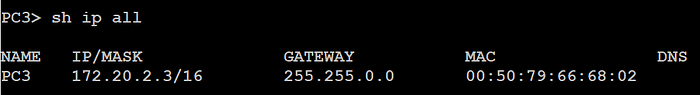
ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol, which is used to discover the MAC address of the directly connected devices. To transmit data from one user to the other, the sender needs two types of addresses L2 (MAC address) and L3 (IP address), as for IP address it is solved by the DNS and DHCP but for the MAC address we need a protocol that can solve this issue, then comes the ARP protocol.
How does ARP work?
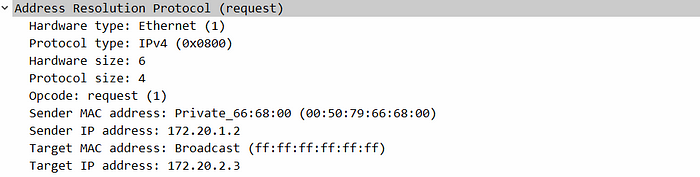
After adding the destination's IP address, the sender has to add the MAC address of the next-hop. Now, the sender initiates an ARP request, it is a broadcast message so every device in the will receive the APR request but the intended recipient only sends an ARP reply, others just discard it. Based on the Target IP the receiver decides whether to respond or discard.
Types of ARP:
- Traditional ARP
- ARP Probe
- Gratuitous ARP
- Proxy ARP
Traditional ARP
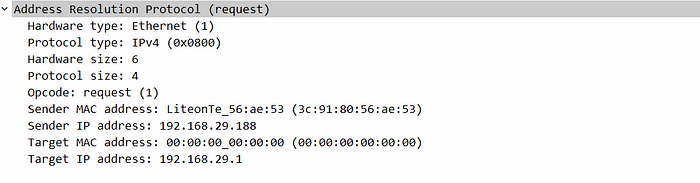
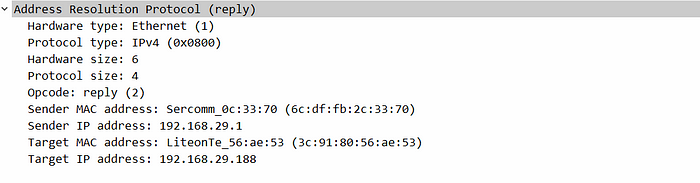
The traditional ARP just sends ARP requests to discover the next-hop MAC address and receives ARP replies for the requests.
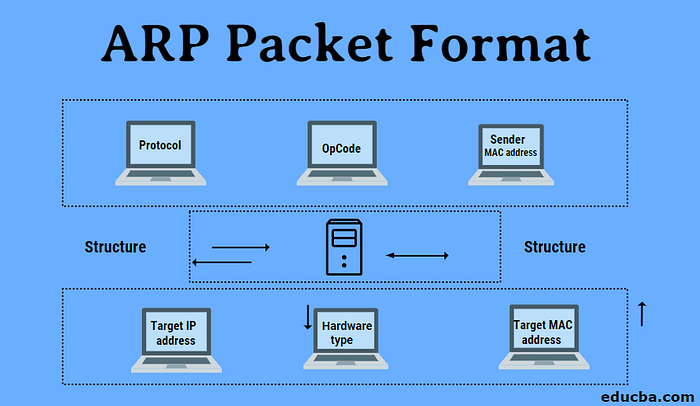
Traditional ARP format
Source MAC: sender’s MAC
Destination MAC: Broadcast
Sender MAC: MAC address of the sender
Sender IP: IP address of the sender
Target MAC: 00:00:00:00:00:00
Target IP: IP address of the next-hop
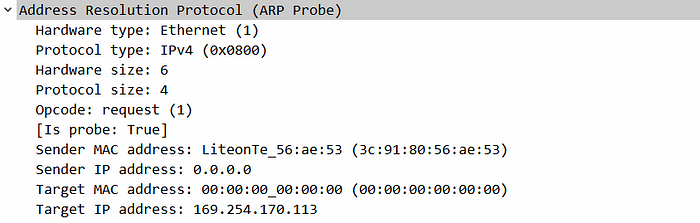
ARP Probe:
ARP Probes are used for duplicate address detection. When a DHCP server receives a discover message it will send an Offer message but before sending the Offer it will send an ARP Probe to verify whether the IP address it is going to offer is already being used or not. The client also receives the Offer message and sends an ARP Prope. ARP Probe is also used by APIPA.
Source MAC: sender’s MAC
Destination MAC: Broadcast
Sender MAC: MAC address of the sender
Sender IP: 0.0.0.0
Target MAC: 00:00:00:00:00:00
Target IP: IP address of the sender

Gratuitous ARP or GARP:
The GARP is used to announce the existence of a node. When a new node connects to the network it sends a GARP to announce its MAC address to the neighbours. It is mostly used in HSPR, VRRP, and GLBP environments. It is also used for Duplicate Address Detection.
Source MAC: sender’s MAC
Destination MAC: Broadcast
Sender MAC: MAC address of the sender
Sender IP: IP address of the sender
Target MAC: ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
Target IP: IP address of the sender

Proxy ARP:
Proxy ARP is the technique in which one host, usually a router, answers ARP requests intended for another machine. By “faking” its identity, the router accepts responsibility for routing packets to the “real” destination. Proxy ARP can help machines on a subnet reach remote subnets without the need to configure routing or a default gateway. Proxy ARP must be used on the network where IP hosts are not configured with a default gateway or do not have any routing intelligence.